在推荐系统的演进历程中,从离线批处理到在线实时更新,是一次质的飞跃。传统的推荐系统依赖历史数据训练模型,更新周期以天甚至周为单位,用户兴趣的快速变化往往被忽略。而实时推荐系统能够在秒级甚至毫秒级响应,捕捉用户行为的即时反馈,动态调整推荐策略。这种能力背后,是流式计算框架、在线学习算法和探索-利用平衡机制的深度融合。
本文将深入探讨实时推荐系统的架构设计、流式计算框架(
Flink/Kafka)的应用、在线学习的基础理论、 Bandit 算法家族( UCB 、
Thompson Sampling 等)、上下文 Bandit 、时变偏好建模( HyperBandit 、
B-DES)、以及 YouTube
和字节跳动等公司的工业实践。每个算法都配有完整的代码实现,每个概念都通过具体例子说明,并在文末提供详细的
Q&A 解答常见疑问。
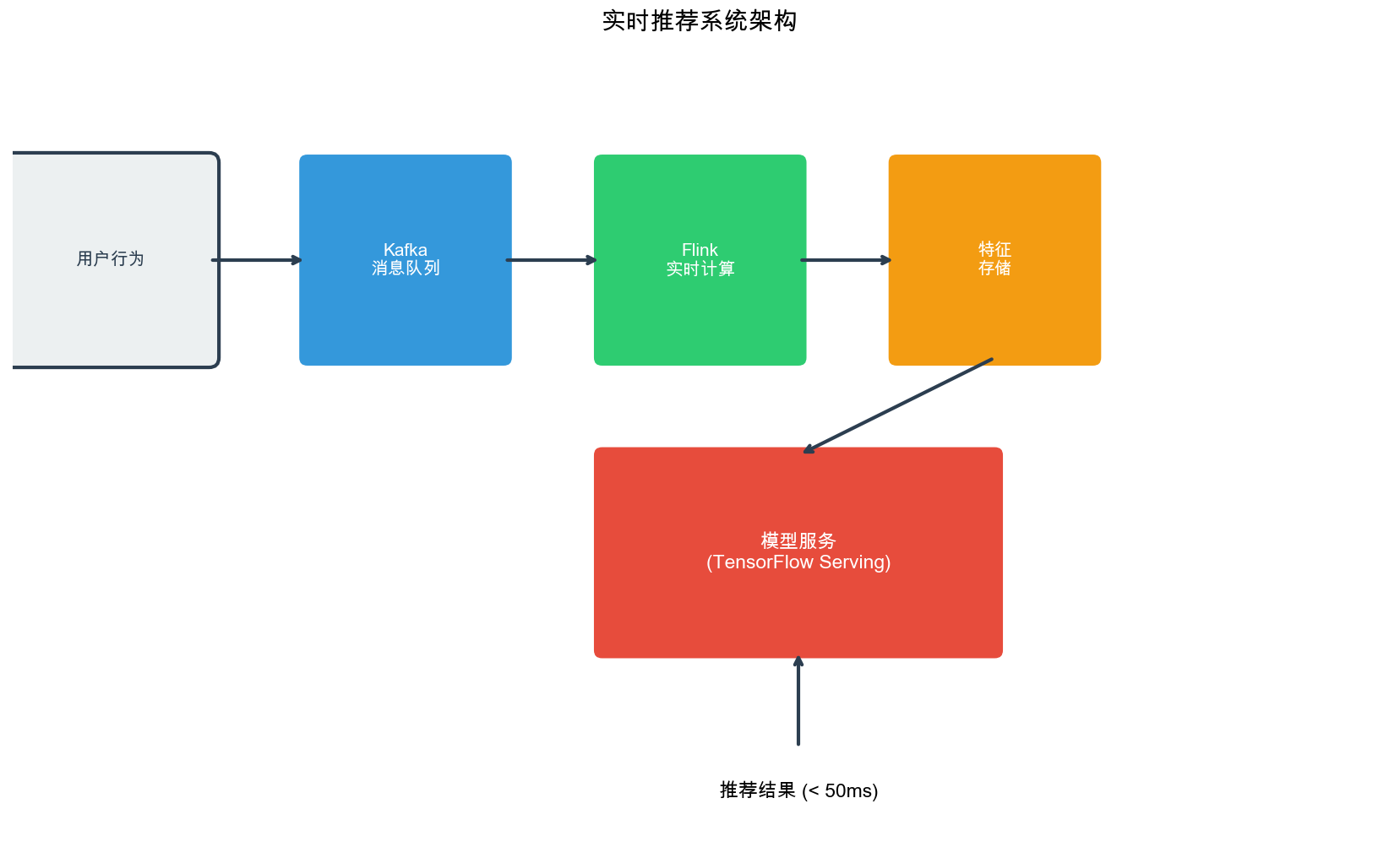
实时推荐系统的架构设计
Lambda 架构与 Kappa 架构
实时推荐系统的架构演进经历了从 Lambda 到 Kappa 的转变。 Lambda
架构采用批处理层和速度层双轨并行,保证数据一致性但增加了系统复杂度;
Kappa 架构统一流处理,简化了架构但对数据重放能力要求更高。
Lambda 架构 包含三个层次:
批处理层( Batch Layer) :使用 MapReduce 或 Spark
处理历史全量数据,生成离线模型和特征速度层( Speed Layer) :使用 Storm 或 Flink
处理实时流数据,快速更新增量特征服务层( Serving
Layer) :合并批处理和流处理的结果,对外提供统一 API
Kappa
架构 则简化为单一流处理管道,所有数据都通过流处理引擎,需要历史数据时通过数据重放实现。
代码目的: 演示 Lambda
架构的批处理层和速度层实现,展示如何同时使用离线批处理和实时流处理来构建推荐系统。
Lambda
架构通过双轨并行保证数据一致性和实时性,是工业级实时推荐系统的经典架构。
整体思路: 1. 批处理层 :使用 Spark
处理历史全量数据,训练离线模型(如 ALS),生成稳定的基础特征 2.
速度层 :使用 Flink
处理实时流数据,快速更新增量特征,捕捉用户行为的即时变化 3.
服务层合并 :将批处理和流处理的结果合并,提供统一的推荐
API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.ml.recommendation import ALSspark = SparkSession.builder.appName("BatchLayer" ).getOrCreate() ratings_df = spark.read.parquet("hdfs://data/ratings" ) als = ALS(maxIter=10 , regParam=0.1 , userCol="userId" , itemCol="itemId" , ratingCol="rating" ) model = als.fit(ratings_df) model.write().overwrite().save("hdfs://models/als_model" ) from pyflink.datastream import StreamExecutionEnvironmentfrom pyflink.table import StreamTableEnvironmentenv = StreamExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment() table_env = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env) table_env.execute_sql(""" CREATE TABLE user_actions ( user_id BIGINT, item_id BIGINT, action_type STRING, timestamp BIGINT, proctime AS PROCTIME() ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'kafka', 'topic' = 'user_actions', 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'localhost:9092', 'format' = 'json' ) """ )realtime_features = table_env.sql_query(""" SELECT user_id, item_id, COUNT(*) as action_count, MAX(timestamp) as last_action_time FROM user_actions WHERE action_type = 'click' GROUP BY user_id, item_id """ )
实时推荐系统的核心组件
一个完整的实时推荐系统通常包含以下组件:
数据采集层 :收集用户行为(点击、浏览、购买等)消息队列 : Kafka 作为缓冲,解耦数据生产和消费流计算引擎 : Flink 进行实时特征计算和模型更新特征存储 : Redis/HBase 存储实时特征模型服务 :在线推理服务,结合实时和离线特征AB 测试平台 :支持多策略对比和效果评估
代码目的:
实现实时推荐系统的核心组件,包括数据采集、特征存储和模型服务。这个示例展示了如何构建一个端到端的实时推荐系统,从用户行为采集到推荐结果返回的完整流程。
整体思路: 1. 数据采集 :使用 Kafka
Producer 将用户行为事件异步发送到消息队列,实现高吞吐量的数据采集 2.
特征存储 :使用 Redis
存储实时特征,支持快速读写和过期策略 3. 模型服务 :使用
Flask 提供 RESTful API,合并实时和离线特征进行推理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import redisimport jsonfrom kafka import KafkaConsumer, KafkaProducerfrom flask import Flask, request, jsonifyproducer = KafkaProducer( bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092' ], value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8' ) ) def log_user_action (user_id, item_id, action_type, timestamp ): event = { 'user_id' : user_id, 'item_id' : item_id, 'action_type' : action_type, 'timestamp' : timestamp } producer.send('user_actions' , value=event) redis_client = redis.Redis(host='localhost' , port=6379 , db=0 ) def update_user_features (user_id, features ): key = f"user_features:{user_id} " redis_client.setex(key, 3600 , json.dumps(features)) def get_user_features (user_id ): key = f"user_features:{user_id} " data = redis_client.get(key) return json.loads(data) if data else {} app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/recommend' , methods=['POST' ] def recommend (): user_id = request.json['user_id' ] realtime_features = get_user_features(user_id) offline_features = get_offline_features(user_id) combined_features = {**offline_features, **realtime_features} recommendations = model.predict(user_id, combined_features) return jsonify({'recommendations' : recommendations})
流式计算框架: Flink 与 Kafka
Kafka:分布式消息队列
Kafka
作为分布式流数据平台,在实时推荐系统中承担数据缓冲和流式传输的角色。其核心概念包括:
Topic :消息主题,按业务划分(如 user_actions 、
item_updates)Partition :分区,实现并行处理和水平扩展Consumer Group :消费者组,实现负载均衡和容错Offset :偏移量,记录消费进度
代码目的: 实现 Kafka
生产者和消费者,展示如何在实时推荐系统中使用 Kafka
进行数据采集和流式处理。 Kafka
的高吞吐量和容错能力使其成为实时推荐系统的核心基础设施。
整体思路: 1.
生产者 :将用户行为事件发送到 Kafka,使用 user_id 作为
key 保证同一用户的事件有序 2. 消费者 :从 Kafka
消费事件,实时统计用户行为并更新特征存储 3.
容错机制 :通过 Consumer Group
实现负载均衡和故障恢复
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 from kafka import KafkaProducerimport jsonimport timeproducer = KafkaProducer( bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092' ], value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8' ), acks='all' , retries=3 ) def send_user_action (user_id, item_id, action_type ): event = { 'user_id' : user_id, 'item_id' : item_id, 'action_type' : action_type, 'timestamp' : int (time.time() * 1000 ) } future = producer.send('user_actions' , key=str (user_id).encode('utf-8' ), value=event) return future.get(timeout=10 ) from kafka import KafkaConsumerfrom collections import defaultdictconsumer = KafkaConsumer( 'user_actions' , bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092' ], group_id='recommendation_processor' , value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8' )), auto_offset_reset='latest' , enable_auto_commit=True ) user_click_counts = defaultdict(int ) for message in consumer: event = message.value user_id = event['user_id' ] if event['action_type' ] == 'click' : user_click_counts[user_id] += 1 update_user_features(user_id, { 'click_count' : user_click_counts[user_id], 'last_click_time' : event['timestamp' ] })
Flink:流式计算引擎
Apache Flink
提供了低延迟、高吞吐的流处理能力,支持事件时间、状态管理和精确一次语义。
Flink 核心概念 :
DataStream :无界数据流Window :时间窗口,支持滚动、滑动、会话窗口State :状态管理,支持键控状态和算子状态Checkpoint :检查点,实现容错
代码目的: 实现基于 Flink
的实时特征计算,展示如何使用 Flink
的状态管理和窗口操作来处理用户行为流,实时计算用户-物品交互特征。 Flink
的状态管理能力使得可以在流处理中维护用户历史行为,实现复杂的实时特征计算。
整体思路: 1. 流数据源 :从 Kafka
读取用户行为事件流 2. 状态管理 :使用 Flink 的
ValueState 存储用户-物品交互历史 3.
特征计算 :实时统计点击次数、浏览次数等特征 4.
特征输出 :将计算好的特征输出到下游系统(如 Redis)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 from pyflink.datastream import StreamExecutionEnvironmentfrom pyflink.datastream.functions import MapFunction, KeyedProcessFunctionfrom pyflink.datastream.window import TumblingEventTimeWindowsfrom pyflink.common.typeinfo import Typesfrom pyflink.common.serialization import SimpleStringSchemafrom pyflink.datastream.connectors import FlinkKafkaConsumerimport jsonenv = StreamExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment() env.set_parallelism(4 ) env.enable_checkpointing(60000 ) kafka_props = { 'bootstrap.servers' : 'localhost:9092' , 'group.id' : 'flink_consumer' } kafka_source = FlinkKafkaConsumer( topics='user_actions' , deserialization_schema=SimpleStringSchema(), properties=kafka_props ) class ParseEvent (MapFunction ): def map (self, value ): return json.loads(value) class UserItemFeatureProcessor (KeyedProcessFunction ): def __init__ (self ): self.state = None def open (self, runtime_context ): from pyflink.datastream.state import ValueStateDescriptor state_desc = ValueStateDescriptor("interaction_state" , Types.PY_DICT) self.state = runtime_context.get_state(state_desc) def process_element (self, value, ctx, out ): user_id = value['user_id' ] item_id = value['item_id' ] action_type = value['action_type' ] timestamp = value['timestamp' ] history = self.state.value() or {} key = f"{user_id} :{item_id} " if key not in history: history[key] = { 'click_count' : 0 , 'view_count' : 0 , 'last_action_time' : timestamp } if action_type == 'click' : history[key]['click_count' ] += 1 elif action_type == 'view' : history[key]['view_count' ] += 1 history[key]['last_action_time' ] = timestamp self.state.update(history) out.collect({ 'user_id' : user_id, 'item_id' : item_id, 'features' : history[key], 'timestamp' : timestamp }) stream = env.add_source(kafka_source) parsed_stream = stream.map (ParseEvent()) keyed_stream = parsed_stream.key_by(lambda x: f"{x['user_id' ]} :{x['item_id' ]} " ) feature_stream = keyed_stream.process(UserItemFeatureProcessor()) feature_stream.print () env.execute("Real-time Feature Computation" )
Flink 窗口操作
窗口操作是流处理的核心,用于在时间维度上聚合数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from pyflink.datastream.window import TumblingEventTimeWindows, SlidingEventTimeWindowsfrom pyflink.datastream.functions import AggregateFunctionfrom pyflink.common import Timeclass ClickCountAggregator (AggregateFunction ): def create_accumulator (self ): return {'click_count' : 0 , 'user_ids' : set ()} def add (self, value, accumulator ): accumulator['click_count' ] += 1 accumulator['user_ids' ].add(value['user_id' ]) return accumulator def get_result (self, accumulator ): return { 'click_count' : accumulator['click_count' ], 'unique_users' : len (accumulator['user_ids' ]) } def merge (self, acc_a, acc_b ): acc_a['click_count' ] += acc_b['click_count' ] acc_a['user_ids' ].update(acc_b['user_ids' ]) return acc_a windowed_stream = parsed_stream \ .filter (lambda x: x['action_type' ] == 'click' ) \ .key_by(lambda x: x['item_id' ]) \ .window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(5 ))) \ .aggregate(ClickCountAggregator()) sliding_window_stream = parsed_stream \ .filter (lambda x: x['action_type' ] == 'click' ) \ .key_by(lambda x: x['item_id' ]) \ .window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(5 ), Time.minutes(1 ))) \ .aggregate(ClickCountAggregator())
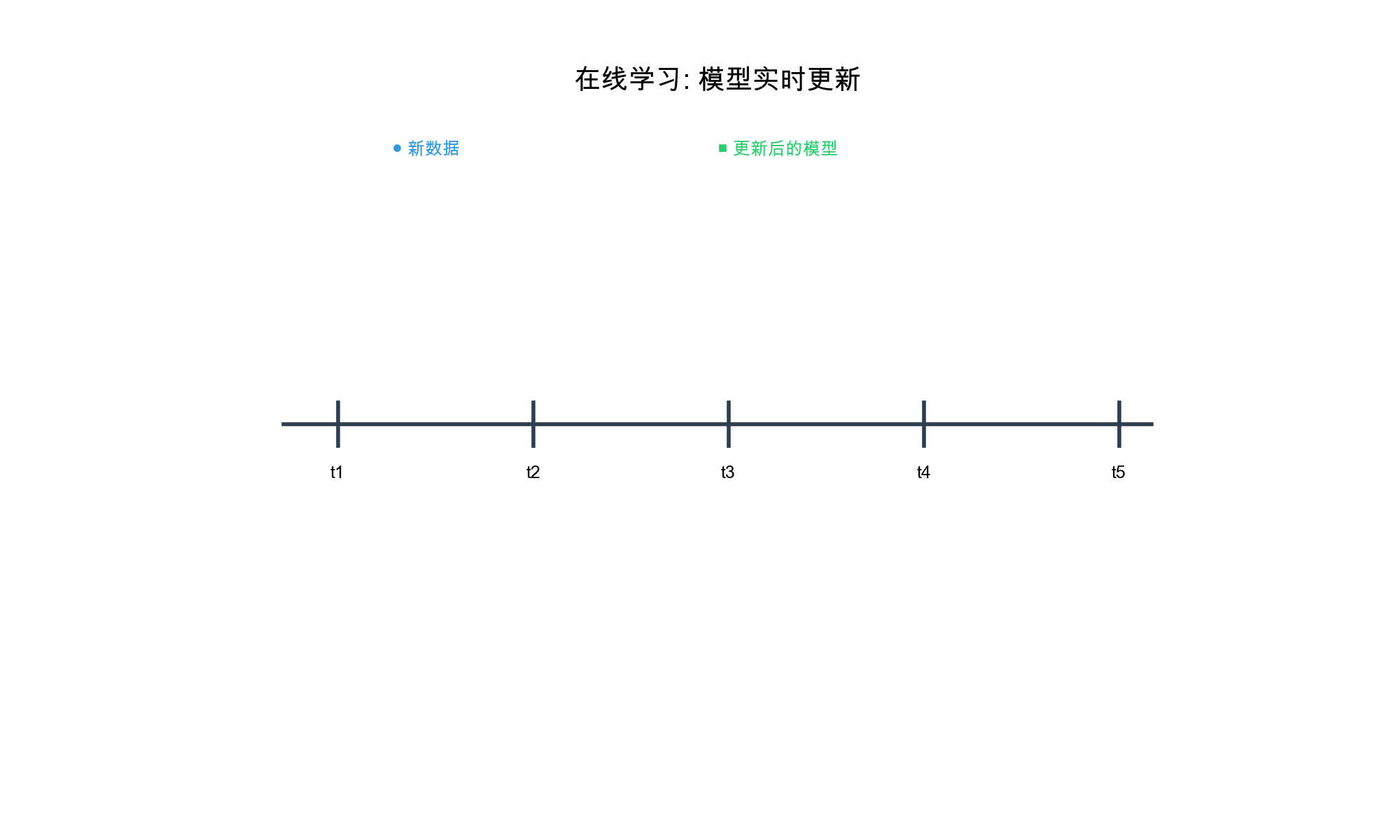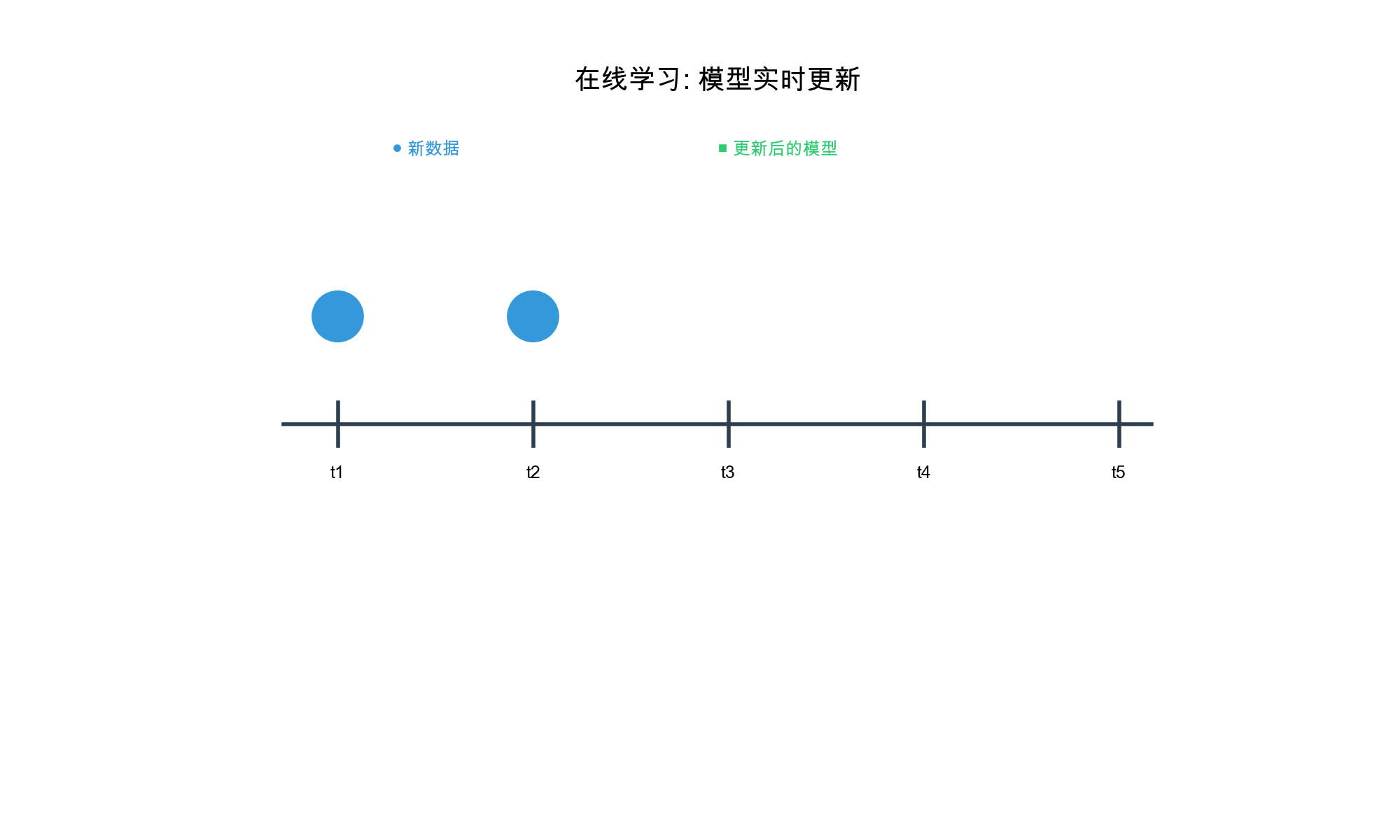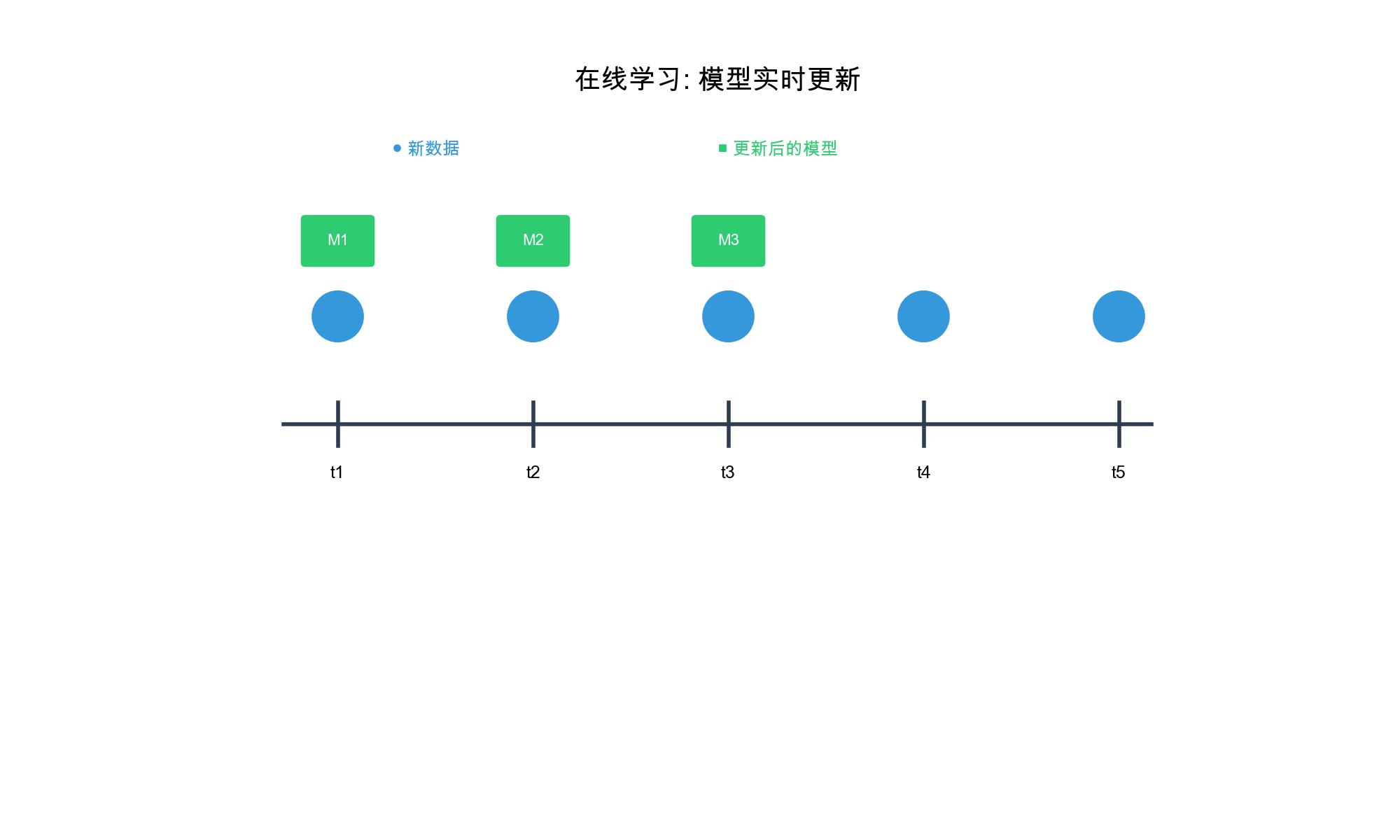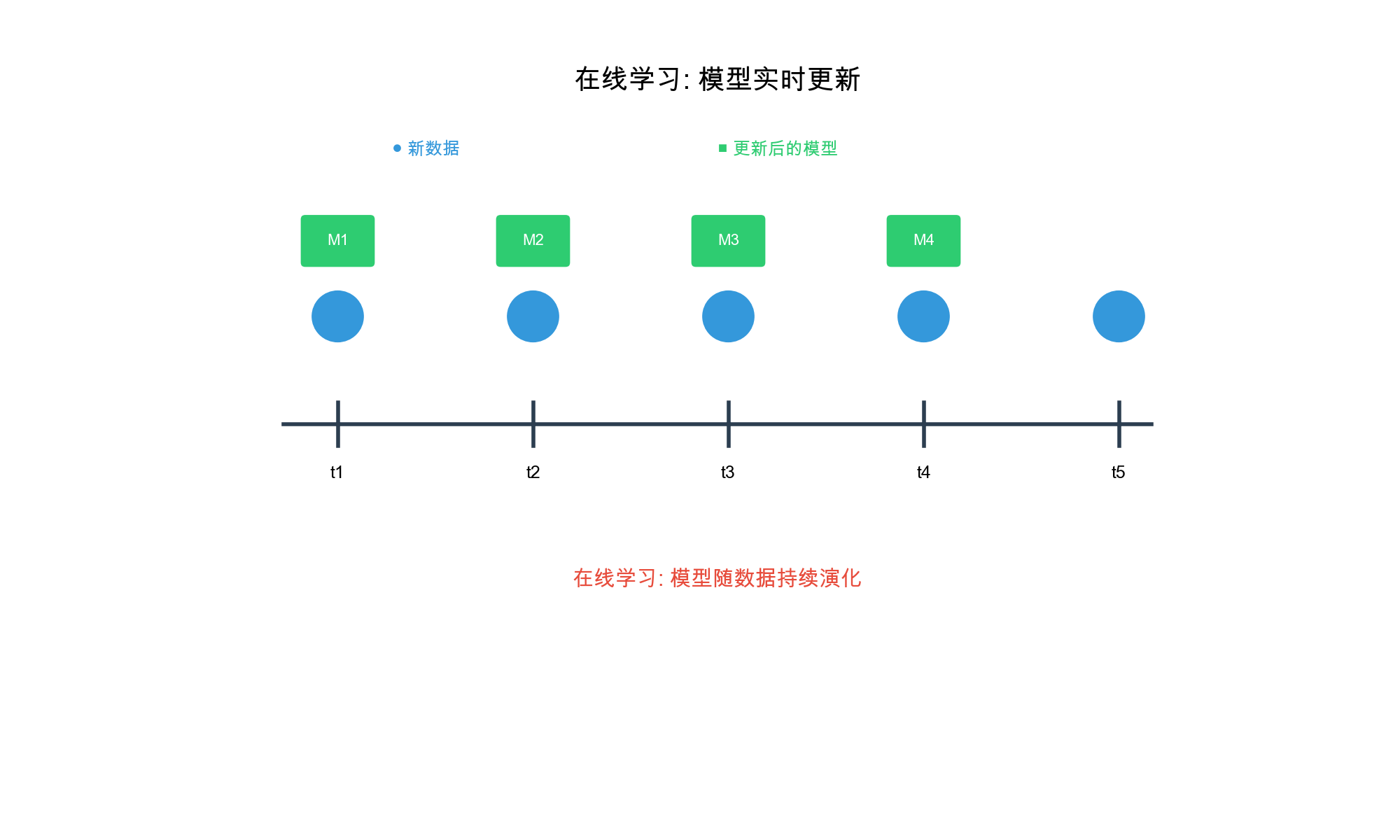
在线学习基础
在线学习 vs 离线学习
在线学习( Online Learning)与传统的离线学习( Batch
Learning)在数据流、模型更新和优化目标上存在本质差异。
离线学习 : - 数据:静态数据集,一次性加载 -
更新:周期性批量重训练 - 优化:最小化历史数据的损失函数 -
延迟:小时到天级别
在线学习 : - 数据:流式数据,逐个或小批量到达 -
更新:增量更新,每个样本或小批量后立即更新 - 优化:最小化累积遗憾(
Regret) - 延迟:毫秒到秒级别
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import numpy as npfrom sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressorX_train = np.load('features.npy' ) y_train = np.load('labels.npy' ) model = SGDRegressor(max_iter=1000 ) model.fit(X_train, y_train) class OnlineLinearModel : def __init__ (self, n_features, learning_rate=0.01 ): self.weights = np.zeros(n_features) self.bias = 0.0 self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.n_samples = 0 def update (self, x, y ): """单个样本更新""" prediction = np.dot(x, self.weights) + self.bias error = y - prediction self.weights += self.learning_rate * error * x self.bias += self.learning_rate * error self.n_samples += 1 return prediction def predict (self, x ): return np.dot(x, self.weights) + self.bias model = OnlineLinearModel(n_features=100 ) for x, y in data_stream: prediction = model.update(x, y)
遗憾( Regret)与累积损失
在线学习的性能评估使用遗憾(
Regret)而非准确率。遗憾定义为算法累积损失与最优策略累积损失的差值。
$$
R_T = {t=1}^T t(a_t) - {a } {t=1}^T _t(a)$$
其中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class RegretTracker : def __init__ (self, actions ): self.actions = actions self.cumulative_loss = {a: 0.0 for a in actions} self.algorithm_loss = 0.0 self.history = [] def update (self, chosen_action, loss ): """更新遗憾""" self.algorithm_loss += loss self.cumulative_loss[chosen_action] += loss best_loss = min (self.cumulative_loss.values()) regret = self.algorithm_loss - best_loss self.history.append({ 'round' : len (self.history) + 1 , 'chosen_action' : chosen_action, 'loss' : loss, 'regret' : regret, 'best_action' : min (self.cumulative_loss, key=self.cumulative_loss.get) }) return regret def get_average_regret (self ): """平均遗憾""" if not self.history: return 0.0 return sum (h['regret' ] for h in self.history) / len (self.history)
Bandit 算法基础
多臂老虎机问题
多臂老虎机( Multi-Armed Bandit,
MAB)问题是在线学习的经典模型。假设有
问题形式化 : - 动作集合:Double subscripts: use braces to clarify r_t _{a_t}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass BanditEnvironment : def __init__ (self, n_arms, reward_distributions ): """ n_arms: 老虎机数量 reward_distributions: 每个老虎机的奖励分布(均值列表) """ self.n_arms = n_arms self.true_means = reward_distributions self.best_arm = np.argmax(self.true_means) self.best_mean = self.true_means[self.best_arm] def pull (self, arm ): """拉动指定老虎机,返回奖励""" return np.random.binomial(1 , self.true_means[arm]) def get_regret (self, chosen_arm ): """计算单轮遗憾""" return self.best_mean - self.true_means[chosen_arm] env = BanditEnvironment(3 , [0.3 , 0.5 , 0.7 ]) print (f"最优老虎机: {env.best_arm} , 最优期望奖励: {env.best_mean} " )for _ in range (10 ): arm = 0 reward = env.pull(arm) regret = env.get_regret(arm) print (f"选择老虎机 {arm} , 获得奖励 {reward} , 遗憾 {regret:.3 f} " )
ε-贪心算法
ε-贪心(ε-Greedy)是最简单的探索-利用平衡策略:以概率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class EpsilonGreedy : def __init__ (self, n_arms, epsilon=0.1 ): self.n_arms = n_arms self.epsilon = epsilon self.counts = np.zeros(n_arms) self.values = np.zeros(n_arms) def select_arm (self ): """选择动作""" if np.random.random() < self.epsilon: return np.random.randint(self.n_arms) else : return np.argmax(self.values) def update (self, chosen_arm, reward ): """更新动作价值估计""" self.counts[chosen_arm] += 1 n = self.counts[chosen_arm] self.values[chosen_arm] += (reward - self.values[chosen_arm]) / n def run_experiment (self, env, n_rounds ): """运行实验""" total_reward = 0 total_regret = 0 rewards_history = [] regrets_history = [] for t in range (n_rounds): arm = self.select_arm() reward = env.pull(arm) regret = env.get_regret(arm) self.update(arm, reward) total_reward += reward total_regret += regret rewards_history.append(total_reward) regrets_history.append(total_regret) return { 'total_reward' : total_reward, 'total_regret' : total_regret, 'rewards_history' : rewards_history, 'regrets_history' : regrets_history } n_rounds = 1000 epsilons = [0.0 , 0.01 , 0.1 , 0.3 ] results = {} for eps in epsilons: algo = EpsilonGreedy(n_arms=3 , epsilon=eps) result = algo.run_experiment(env, n_rounds) results[eps] = result print (f"ε={eps} : 总奖励={result['total_reward' ]} , 总遗憾={result['total_regret' ]:.2 f} " )
UCB 算法
上置信界( Upper Confidence Bound,
UCB)算法通过置信区间平衡探索和利用。 UCB
选择具有最高上置信界的动作,既考虑当前估计值,也考虑不确定性。
UCB1 算法
UCB1 的置信界公式为:
$$
UCB(a) = {}_a + c $$
其中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class UCB1 : def __init__ (self, n_arms, c=1.414 ): self.n_arms = n_arms self.c = c self.counts = np.zeros(n_arms) self.values = np.zeros(n_arms) self.total_counts = 0 def select_arm (self ): """选择 UCB 值最大的动作""" if self.total_counts < self.n_arms: return int (self.total_counts) ucb_values = self.values + self.c * np.sqrt( np.log(self.total_counts) / self.counts ) return np.argmax(ucb_values) def update (self, chosen_arm, reward ): """更新动作价值""" self.counts[chosen_arm] += 1 self.total_counts += 1 n = self.counts[chosen_arm] self.values[chosen_arm] += (reward - self.values[chosen_arm]) / n def run_experiment (self, env, n_rounds ): """运行实验""" total_reward = 0 total_regret = 0 regrets_history = [] for t in range (n_rounds): arm = self.select_arm() reward = env.pull(arm) regret = env.get_regret(arm) self.update(arm, reward) total_reward += reward total_regret += regret regrets_history.append(total_regret) return { 'total_reward' : total_reward, 'total_regret' : total_regret, 'regrets_history' : regrets_history } ucb_algo = UCB1(n_arms=3 , c=1.414 ) ucb_result = ucb_algo.run_experiment(env, n_rounds=1000 ) print (f"UCB1 总遗憾: {ucb_result['total_regret' ]:.2 f} " )
UCB2 算法
UCB2 通过更精细的置信界改进
UCB1,特别适用于奖励分布差异较大的场景。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class UCB2 : def __init__ (self, n_arms, alpha=0.5 ): self.n_arms = n_arms self.alpha = alpha self.counts = np.zeros(n_arms) self.values = np.zeros(n_arms) self.r = np.zeros(n_arms, dtype=int ) self.total_counts = 0 def tau (self, r ): """计算阶段长度""" return int (np.ceil((1 + self.alpha) ** r)) def select_arm (self ): if self.total_counts < self.n_arms: return int (self.total_counts) ucb_values = [] for a in range (self.n_arms): tau_r = self.tau(self.r[a]) if self.counts[a] >= tau_r: self.r[a] += 1 tau_r = self.tau(self.r[a]) bonus = np.sqrt( (1 + self.alpha) * np.log(np.e * self.total_counts / tau_r) / (2 * tau_r) ) ucb_values.append(self.values[a] + bonus) return np.argmax(ucb_values) def update (self, chosen_arm, reward ): self.counts[chosen_arm] += 1 self.total_counts += 1 n = self.counts[chosen_arm] self.values[chosen_arm] += (reward - self.values[chosen_arm]) / n
Thompson Sampling
Thompson Sampling(
TS)是贝叶斯方法,通过采样后验分布选择动作。对于伯努利奖励,使用 Beta
分布作为共轭先验。
Beta-Bernoulli Thompson
Sampling
假设奖励
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 class ThompsonSampling : def __init__ (self, n_arms, alpha=1.0 , beta=1.0 ): """ alpha, beta: Beta 分布的超参数(先验) alpha=beta=1 对应均匀先验 """ self.n_arms = n_arms self.alpha = np.ones(n_arms) * alpha self.beta = np.ones(n_arms) * beta def select_arm (self ): """从每个动作的后验分布采样,选择采样值最大的动作""" samples = np.random.beta(self.alpha, self.beta) return np.argmax(samples) def update (self, chosen_arm, reward ): """更新 Beta 分布参数""" if reward == 1 : self.alpha[chosen_arm] += 1 else : self.beta[chosen_arm] += 1 def get_posterior_mean (self, arm ): """获取后验均值""" return self.alpha[arm] / (self.alpha[arm] + self.beta[arm]) def run_experiment (self, env, n_rounds ): """运行实验""" total_reward = 0 total_regret = 0 regrets_history = [] posterior_means_history = [] for t in range (n_rounds): arm = self.select_arm() reward = env.pull(arm) regret = env.get_regret(arm) self.update(arm, reward) total_reward += reward total_regret += regret regrets_history.append(total_regret) means = [self.get_posterior_mean(a) for a in range (self.n_arms)] posterior_means_history.append(means) return { 'total_reward' : total_reward, 'total_regret' : total_regret, 'regrets_history' : regrets_history, 'posterior_means_history' : posterior_means_history } ts_algo = ThompsonSampling(n_arms=3 , alpha=1.0 , beta=1.0 ) ts_result = ts_algo.run_experiment(env, n_rounds=1000 ) print (f"Thompson Sampling 总遗憾: {ts_result['total_regret' ]:.2 f} " )import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig, axes = plt.subplots(1 , 3 , figsize=(15 , 4 )) for arm in range (3 ): ax = axes[arm] from scipy.stats import beta x = np.linspace(0 , 1 , 100 ) y = beta.pdf(x, ts_algo.alpha[arm], ts_algo.beta[arm]) ax.plot(x, y, label=f'后验分布' ) ax.axvline(env.true_means[arm], color='r' , linestyle='--' , label=f'真实均值={env.true_means[arm]} ' ) ax.set_title(f'老虎机 {arm} ' ) ax.legend() plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
高斯 Thompson Sampling
对于连续奖励,使用高斯-高斯共轭先验:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class GaussianThompsonSampling : def __init__ (self, n_arms, mu_0=0.0 , lambda_0=1.0 , alpha_0=1.0 , beta_0=1.0 ): """ 高斯-逆 Gamma 共轭先验 mu_0: 先验均值 lambda_0: 先验精度(样本数) alpha_0, beta_0: 逆 Gamma 分布参数 """ self.n_arms = n_arms self.mu = np.ones(n_arms) * mu_0 self.lambda_param = np.ones(n_arms) * lambda_0 self.alpha = np.ones(n_arms) * alpha_0 self.beta = np.ones(n_arms) * beta_0 def select_arm (self ): """从后验分布采样均值和方差,然后采样奖励""" samples = [] for a in range (self.n_arms): tau = np.random.gamma(self.alpha[a], 1.0 / self.beta[a]) sigma_sq = 1.0 / tau mu_sample = np.random.normal( self.mu[a], np.sqrt(sigma_sq / self.lambda_param[a]) ) samples.append(mu_sample) return np.argmax(samples) def update (self, chosen_arm, reward ): """更新后验参数""" n = self.lambda_param[chosen_arm] self.mu[chosen_arm] = (n * self.mu[chosen_arm] + reward) / (n + 1 ) self.lambda_param[chosen_arm] += 1 n_new = self.lambda_param[chosen_arm] self.beta[chosen_arm] += 0.5 * n / (n + 1 ) * (reward - self.mu[chosen_arm]) ** 2 self.alpha[chosen_arm] += 0.5
Contextual Bandit
上下文 Bandit( Contextual Bandit)在 MAB
基础上引入上下文信息,根据当前上下文选择动作。
线性上下文 Bandit
假设奖励是上下文的线性函数:
LinUCB 算法 使用线性回归估计参数,并计算置信界:
$$
UCB(a) = _a^T x + $$
其中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class LinUCB : def __init__ (self, n_arms, n_features, alpha=1.0 ): """ n_arms: 动作数量 n_features: 上下文特征维度 alpha: 置信参数 """ self.n_arms = n_arms self.n_features = n_features self.alpha = alpha self.A = [np.eye(n_features) for _ in range (n_arms)] self.b = [np.zeros(n_features) for _ in range (n_arms)] self.theta = [np.zeros(n_features) for _ in range (n_arms)] def select_arm (self, context ): """根据上下文选择动作""" ucb_values = [] for a in range (self.n_arms): self.theta[a] = np.linalg.solve(self.A[a], self.b[a]) A_inv = np.linalg.inv(self.A[a]) ucb = np.dot(self.theta[a], context) + \ self.alpha * np.sqrt(np.dot(context, np.dot(A_inv, context))) ucb_values.append(ucb) return np.argmax(ucb_values) def update (self, chosen_arm, context, reward ): """更新模型参数""" self.A[chosen_arm] += np.outer(context, context) self.b[chosen_arm] += reward * context self.theta[chosen_arm] = np.linalg.solve(self.A[chosen_arm], self.b[chosen_arm]) n_features = 10 linucb = LinUCB(n_arms=5 , n_features=n_features, alpha=1.0 ) for t in range (1000 ): context = np.random.randn(n_features) arm = linucb.select_arm(context) true_theta = np.random.randn(n_features) reward = np.dot(true_theta, context) + np.random.normal(0 , 0.1 ) linucb.update(arm, context, reward)
神经网络上下文 Bandit
对于非线性关系,使用神经网络建模:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.optim as optimclass NeuralUCB (nn.Module): def __init__ (self, n_features, n_arms, hidden_dim=64 ): super (NeuralUCB, self).__init__() self.n_arms = n_arms self.n_features = n_features self.feature_extractor = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(n_features, hidden_dim), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim), nn.ReLU() ) self.heads = nn.ModuleList([ nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim // 2 ), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden_dim // 2 , 1 ) ) for _ in range (n_arms) ) def forward (self, context ): """前向传播,返回每个动作的预测值""" features = self.feature_extractor(context) outputs = [head(features) for head in self.heads] return torch.cat(outputs, dim=1 ) def select_arm (self, context, alpha=1.0 ): """选择动作(需要计算不确定性)""" self.eval () with torch.no_grad(): predictions = self.forward(context) uncertainties = torch.ones_like(predictions) * alpha ucb_values = predictions + uncertainties return torch.argmax(ucb_values).item() class NeuralUCBAgent : def __init__ (self, n_features, n_arms, learning_rate=0.001 ): self.model = NeuralUCB(n_features, n_arms) self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) self.criterion = nn.MSELoss() self.contexts = [] self.arms = [] self.rewards = [] def select_arm (self, context ): context_tensor = torch.FloatTensor(context).unsqueeze(0 ) return self.model.select_arm(context_tensor) def update (self, context, arm, reward ): """更新模型""" self.contexts.append(context) self.arms.append(arm) self.rewards.append(reward) if len (self.contexts) % 10 == 0 : self.train_batch() def train_batch (self ): """批量训练""" if len (self.contexts) < 10 : return contexts_tensor = torch.FloatTensor(self.contexts[-100 :]) arms_tensor = torch.LongTensor(self.arms[-100 :]) rewards_tensor = torch.FloatTensor(self.rewards[-100 :]) self.model.train() self.optimizer.zero_grad() predictions = self.model(contexts_tensor) selected_predictions = predictions.gather(1 , arms_tensor.unsqueeze(1 )).squeeze() loss = self.criterion(selected_predictions, rewards_tensor) loss.backward() self.optimizer.step()
HyperBandit:时变偏好建模
用户兴趣会随时间变化, HyperBandit
通过超参数化建模捕捉这种时变特性。
时变偏好的数学建模
假设用户偏好
其中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 class HyperBandit : def __init__ (self, n_arms, n_features, time_decay=0.95 ): """ time_decay: 时间衰减因子,控制历史信息的重要性 """ self.n_arms = n_arms self.n_features = n_features self.time_decay = time_decay self.theta_history = {a: [] for a in range (n_arms)} self.time_history = {a: [] for a in range (n_arms)} self.theta = [np.random.randn(n_features) * 0.1 for _ in range (n_arms)] self.A = [np.eye(n_features) for _ in range (n_arms)] self.b = [np.zeros(n_features) for _ in range (n_arms)] def get_time_weight (self, t_current, t_past ): """计算时间权重""" return self.time_decay ** (t_current - t_past) def update_theta (self, arm, current_time ): """更新时变参数估计""" if len (self.time_history[arm]) == 0 : return A_weighted = np.eye(self.n_features) b_weighted = np.zeros(self.n_features) for i, (theta_old, t_old, reward, context) in enumerate ( zip (self.theta_history[arm], self.time_history[arm], self.reward_history[arm], self.context_history[arm]) ): weight = self.get_time_weight(current_time, t_old) A_weighted += weight * np.outer(context, context) b_weighted += weight * reward * context self.theta[arm] = np.linalg.solve(A_weighted, b_weighted) self.A[arm] = A_weighted self.b[arm] = b_weighted def select_arm (self, context, current_time, alpha=1.0 ): """选择动作""" ucb_values = [] for a in range (self.n_arms): self.update_theta(a, current_time) A_inv = np.linalg.inv(self.A[a]) ucb = np.dot(self.theta[a], context) + \ alpha * np.sqrt(np.dot(context, np.dot(A_inv, context))) ucb_values.append(ucb) return np.argmax(ucb_values) def update (self, chosen_arm, context, reward, current_time ): """更新历史记录""" self.theta_history[chosen_arm].append(self.theta[chosen_arm].copy()) self.time_history[chosen_arm].append(current_time) if not hasattr (self, 'reward_history' ): self.reward_history = {a: [] for a in range (self.n_arms)} self.context_history = {a: [] for a in range (self.n_arms)} self.reward_history[chosen_arm].append(reward) self.context_history[chosen_arm].append(context.copy())
B-DES:演化状态建模
B-DES( Bandit with Dynamic Evolving
States)进一步扩展,显式建模状态的演化过程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 class BDES : def __init__ (self, n_arms, n_states, state_dim, transition_rate=0.1 ): """ n_states: 状态数量 state_dim: 状态特征维度 transition_rate: 状态转移率 """ self.n_arms = n_arms self.n_states = n_states self.state_dim = state_dim self.transition_rate = transition_rate self.Q = np.random.randn(n_states, n_arms) * 0.1 self.transition_probs = np.ones((n_states, n_arms, n_states)) / n_states self.state_distribution = np.ones(n_states) / n_states self.state_features = np.random.randn(n_states, state_dim) def evolve_state (self, current_state, action ): """状态演化""" probs = self.transition_probs[current_state, action] new_state = np.random.choice(self.n_states, p=probs) return new_state def update_transition (self, old_state, action, new_state, learning_rate=0.01 ): """更新状态转移概率""" for s in range (self.n_states): if s == old_state: self.transition_probs[old_state, action, s] += learning_rate else : self.transition_probs[old_state, action, s] *= (1 - learning_rate) total = np.sum (self.transition_probs[old_state, action]) self.transition_probs[old_state, action] /= total def select_arm (self, current_state_distribution=None ): """选择动作""" if current_state_distribution is None : current_state_distribution = self.state_distribution expected_values = np.dot(current_state_distribution, self.Q) return np.argmax(expected_values) def update (self, state, action, reward, new_state ): """更新 Q 值和转移概率""" learning_rate = 0.1 discount = 0.9 max_future_q = np.max (self.Q[new_state]) self.Q[state, action] += learning_rate * ( reward + discount * max_future_q - self.Q[state, action] ) self.update_transition(state, action, new_state) self.state_distribution[new_state] += 0.1 self.state_distribution /= np.sum (self.state_distribution)
YouTube 实时推荐系统
YouTube
的实时推荐系统是工业界的经典案例,其架构包含多个关键组件。
系统架构
特征服务 :实时特征(观看历史、搜索历史)和离线特征(用户画像、物品特征)候选生成 :快速召回,从百万级视频中筛选出数百个候选排序模型 :深度神经网络,结合多类特征进行精排在线学习 :实时更新模型参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 class YouTubeRecommendationSystem : def __init__ (self ): self.user_features = {} self.video_features = {} self.candidate_model = None self.ranking_model = None self.online_learner = None def get_user_features (self, user_id ): """获取用户特征""" realtime_features = self.user_features.get(user_id, { 'recent_watches' : [], 'recent_searches' : [], 'watch_time_today' : 0 }) offline_features = { 'age' : 25 , 'gender' : 'M' , 'location' : 'US' } return {**offline_features, **realtime_features} def candidate_generation (self, user_id, n_candidates=500 ): """候选生成""" user_features = self.get_user_features(user_id) candidates = [] recent_watches = user_features.get('recent_watches' , []) for video_id in recent_watches[-10 :]: similar_videos = self.find_similar_videos(video_id, n=50 ) candidates.extend(similar_videos) popular_videos = self.get_popular_videos(n=100 ) candidates.extend(popular_videos) candidates = list (set (candidates))[:n_candidates] return candidates def ranking (self, user_id, candidates ): """排序""" user_features = self.get_user_features(user_id) scores = [] for video_id in candidates: video_features = self.video_features.get(video_id, {}) features = self.extract_features(user_features, video_features) score = self.ranking_model.predict(features) scores.append((video_id, score)) scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[1 ], reverse=True ) return [vid for vid, _ in scores[:20 ]] def extract_features (self, user_features, video_features ): """特征提取""" features = [] features.append(user_features.get('age' , 0 )) features.append(1.0 if user_features.get('gender' ) == 'M' else 0.0 ) features.append(video_features.get('duration' , 0 )) features.append(video_features.get('views' , 0 )) features.append(video_features.get('likes' , 0 )) watch_time = user_features.get('watch_time_today' , 0 ) features.append(watch_time * video_features.get('duration' , 0 )) return np.array(features) def online_update (self, user_id, video_id, label ): """在线更新""" user_features = self.get_user_features(user_id) video_features = self.video_features.get(video_id, {}) features = self.extract_features(user_features, video_features) self.online_learner.update(features, label) if user_id not in self.user_features: self.user_features[user_id] = {'recent_watches' : []} if label == 1 : self.user_features[user_id]['recent_watches' ].append(video_id) self.user_features[user_id]['recent_watches' ] = \ self.user_features[user_id]['recent_watches' ][-100 :]
Interest
Clock:字节跳动的兴趣时钟
字节跳动的 Interest Clock
模型通过时间衰减机制建模用户兴趣的演化。
Interest Clock 原理
Interest Clock
将用户兴趣建模为多个"时钟",每个时钟对应一个兴趣维度,随时间衰减:
$$
I_t(d) = _{i} w_i (-_i (t - t_i))$$
其中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 class InterestClock : def __init__ (self, n_dimensions, decay_rates=None ): """ n_dimensions: 兴趣维度数量(如:科技、娱乐、体育等) decay_rates: 每个维度的衰减率 """ self.n_dimensions = n_dimensions self.decay_rates = decay_rates or [0.1 ] * n_dimensions self.events = {d: [] for d in range (n_dimensions)} self.current_time = 0 def add_event (self, dimension, weight, timestamp=None ): """添加兴趣事件""" if timestamp is None : timestamp = self.current_time self.events[dimension].append({ 'weight' : weight, 'timestamp' : timestamp }) def get_interest (self, dimension, current_time=None ): """计算当前兴趣强度""" if current_time is None : current_time = self.current_time interest = 0.0 decay_rate = self.decay_rates[dimension] for event in self.events[dimension]: time_diff = current_time - event['timestamp' ] if time_diff >= 0 : interest += event['weight' ] * np.exp(-decay_rate * time_diff) return interest def get_all_interests (self, current_time=None ): """获取所有维度的兴趣强度""" return [self.get_interest(d, current_time) for d in range (self.n_dimensions)] def recommend (self, items, current_time=None ): """基于兴趣时钟推荐""" interests = self.get_all_interests(current_time) scores = [] for item in items: item_vector = item['features' ] match_score = np.dot(interests, item_vector) scores.append((item['id' ], match_score)) scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[1 ], reverse=True ) return [item_id for item_id, _ in scores] clock = InterestClock(n_dimensions=5 , decay_rates=[0.1 , 0.15 , 0.2 , 0.1 , 0.12 ]) clock.current_time = 0 clock.add_event(0 , weight=1.0 , timestamp=0 ) clock.add_event(1 , weight=0.8 , timestamp=5 ) for t in range (0 , 20 , 2 ): interests = clock.get_all_interests(t) print (f"时间 {t} : 兴趣强度 = {interests} " )
探索-利用平衡
探索-利用平衡( Exploration-Exploitation
Trade-off)是在线学习的核心问题。
理论界限
Lai-Robbins 下界 :对于
其中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 def compare_algorithms (env, n_rounds=1000 ): """对比不同算法的性能""" algorithms = { 'ε-Greedy (ε=0.1)' : EpsilonGreedy(n_arms=env.n_arms, epsilon=0.1 ), 'UCB1' : UCB1(n_arms=env.n_arms), 'Thompson Sampling' : ThompsonSampling(n_arms=env.n_arms) } results = {} for name, algo in algorithms.items(): result = algo.run_experiment(env, n_rounds) results[name] = result['regrets_history' ] plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 6 )) for name, regrets in results.items(): plt.plot(regrets, label=name) plt.xlabel('轮数' ) plt.ylabel('累积遗憾' ) plt.title('不同算法的探索-利用平衡对比' ) plt.legend() plt.grid(True ) plt.show() return results results = compare_algorithms(env, n_rounds=1000 )
完整代码实现:实时推荐系统
下面是一个完整的实时推荐系统实现,整合了上述所有组件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 import numpy as npimport redisimport jsonfrom kafka import KafkaProducer, KafkaConsumerfrom collections import defaultdictimport threadingimport timeclass RealTimeRecommendationSystem : def __init__ (self, redis_host='localhost' , redis_port=6379 , kafka_servers=['localhost:9092' ] ): self.redis_client = redis.Redis(host=redis_host, port=redis_port, db=0 ) self.producer = KafkaProducer( bootstrap_servers=kafka_servers, value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8' ) ) self.user_features = {} self.models = {} self.item_features = {} self.online_learners = {} def get_user_model (self, user_id, n_features=100 ): """获取或创建用户的推荐模型""" if user_id not in self.models: self.models[user_id] = LinUCB( n_arms=1000 , n_features=n_features, alpha=1.0 ) return self.models[user_id] def update_user_features (self, user_id, event ): """更新用户实时特征""" if user_id not in self.user_features: self.user_features[user_id] = { 'recent_clicks' : [], 'recent_views' : [], 'click_count_today' : 0 , 'last_action_time' : 0 } action_type = event['action_type' ] item_id = event['item_id' ] timestamp = event['timestamp' ] if action_type == 'click' : self.user_features[user_id]['recent_clicks' ].append(item_id) self.user_features[user_id]['recent_clicks' ] = \ self.user_features[user_id]['recent_clicks' ][-50 :] self.user_features[user_id]['click_count_today' ] += 1 elif action_type == 'view' : self.user_features[user_id]['recent_views' ].append(item_id) self.user_features[user_id]['recent_views' ] = \ self.user_features[user_id]['recent_views' ][-100 :] self.user_features[user_id]['last_action_time' ] = timestamp self.redis_client.setex( f"user_features:{user_id} " , 3600 , json.dumps(self.user_features[user_id]) ) def extract_context (self, user_id, item_id ): """提取上下文特征""" user_feat = self.user_features.get(user_id, {}) item_feat = self.item_features.get(item_id, {}) context = [] context.append(user_feat.get('click_count_today' , 0 )) context.append(len (user_feat.get('recent_clicks' , []))) context.append(item_feat.get('popularity' , 0 )) context.append(item_feat.get('category' , 0 )) if item_id in user_feat.get('recent_clicks' , []): context.append(1.0 ) else : context.append(0.0 ) while len (context) < 100 : context.append(0.0 ) return np.array(context[:100 ]) def recommend (self, user_id, n_recommendations=20 ): """生成推荐""" model = self.get_user_model(user_id) candidate_items = list (self.item_features.keys())[:1000 ] scores = [] for item_id in candidate_items: context = self.extract_context(user_id, item_id) ucb_value = model.select_arm(context) scores.append((item_id, ucb_value)) scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[1 ], reverse=True ) recommendations = [item_id for item_id, _ in scores[:n_recommendations]] return recommendations def process_feedback (self, user_id, item_id, reward ): """处理用户反馈""" context = self.extract_context(user_id, item_id) model = self.get_user_model(user_id) arm = hash (item_id) % 1000 model.update(arm, context, reward) log_event = { 'user_id' : user_id, 'item_id' : item_id, 'reward' : reward, 'timestamp' : int (time.time() * 1000 ) } self.producer.send('recommendation_feedback' , value=log_event) def start_consumer (self ): """启动 Kafka 消费者,处理用户行为流""" consumer = KafkaConsumer( 'user_actions' , bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092' ], group_id='recommendation_system' , value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8' )) ) for message in consumer: event = message.value user_id = event['user_id' ] item_id = event['item_id' ] action_type = event['action_type' ] self.update_user_features(user_id, event) if action_type == 'click' : self.process_feedback(user_id, item_id, reward=1.0 ) elif action_type == 'view' : self.process_feedback(user_id, item_id, reward=0.1 ) system = RealTimeRecommendationSystem() for i in range (1000 ): system.item_features[i] = { 'popularity' : np.random.rand(), 'category' : np.random.randint(0 , 10 ) } consumer_thread = threading.Thread(target=system.start_consumer) consumer_thread.daemon = True consumer_thread.start() user_id = 12345 recommendations = system.recommend(user_id, n_recommendations=20 ) print (f"为用户 {user_id} 推荐: {recommendations} " )
Q&A:常见问题解答
Q1:
实时推荐系统与离线推荐系统的主要区别是什么?
A : 主要区别体现在三个方面:
数据流 :离线系统使用静态数据集,实时系统处理流式数据更新频率 :离线系统通常每天或每周更新一次,实时系统可以秒级更新特征时效性 :实时系统能够捕捉用户的最新行为,离线系统只能使用历史数据
实时系统的优势是能够快速响应用户兴趣变化,但需要更复杂的架构和更高的计算资源。
Q2: Flink 和 Spark
Streaming 有什么区别?
A : 主要区别:
处理模型 : Flink 是真正的流处理(逐事件处理),
Spark Streaming 是微批处理(小批量处理)延迟 : Flink 延迟更低(毫秒级), Spark Streaming
延迟较高(秒级)状态管理 : Flink
的状态管理更完善,支持复杂的状态操作容错 : Flink 使用检查点机制, Spark Streaming 依赖
RDD 的容错
对于实时推荐系统, Flink 通常更适合低延迟场景。
Q3: UCB 和 Thompson
Sampling 哪个更好?
A : 两者各有优势:
UCB :理论保证更强,遗憾上界明确,实现简单Thompson
Sampling :实际效果通常更好,探索更自然,但理论分析更复杂
选择建议: - 需要理论保证的场景选 UCB - 实际应用中 Thompson Sampling
往往表现更好 - 可以同时实现两者,通过 AB 测试选择
Q4: 如何处理冷启动问题?
A : 冷启动可以从多个角度解决:
内容特征 :使用物品的内容特征(类别、标签等)进行推荐热门物品 :新用户先推荐热门物品,收集反馈探索策略 :增加探索比例,快速学习用户兴趣迁移学习 :利用相似用户的数据初始化模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def recommend_for_cold_start_user (user_id, user_profile=None ): """为新用户推荐""" if user_profile is None : return get_popular_items(n=20 ) if 'age' in user_profile and 'gender' in user_profile: similar_users = find_similar_user_group(user_profile) return get_items_from_users(similar_users, n=20 ) return get_popular_items(n=20 )
Q5:
在线学习如何保证模型稳定性?
A : 保证稳定性的方法:
学习率衰减 :随时间降低学习率正则化 :防止参数过大滑动窗口 :只使用最近的数据集成方法 :维护多个模型,投票决定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class StableOnlineLearner : def __init__ (self, initial_lr=0.1 , decay_rate=0.99 , regularization=0.01 ): self.learning_rate = initial_lr self.decay_rate = decay_rate self.regularization = regularization self.weights = np.zeros(100 ) self.step = 0 def update (self, x, y ): """稳定更新""" self.step += 1 current_lr = self.learning_rate * (self.decay_rate ** self.step) pred = np.dot(self.weights, x) error = y - pred gradient = -error * x + self.regularization * self.weights self.weights -= current_lr * gradient return pred
Q6: 如何处理数据分布漂移?
A : 数据分布漂移是实时系统的常见问题,解决方法:
检测漂移 :监控模型性能指标,检测准确率下降自适应学习率 :根据数据分布调整学习率重训练 :定期使用最新数据重训练模型集成新旧模型 :同时维护多个版本的模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class DriftAdaptiveModel : def __init__ (self ): self.model = OnlineLinearModel(100 ) self.performance_history = [] self.drift_threshold = 0.1 def detect_drift (self ): """检测数据漂移""" if len (self.performance_history) < 10 : return False recent_perf = np.mean(self.performance_history[-5 :]) old_perf = np.mean(self.performance_history[-10 :-5 ]) return (old_perf - recent_perf) > self.drift_threshold def update (self, x, y ): """更新并检测漂移""" pred = self.model.update(x, y) accuracy = 1.0 if abs (pred - y) < 0.1 else 0.0 self.performance_history.append(accuracy) if self.detect_drift(): self.model.learning_rate *= 2 return pred
Q7:
实时推荐系统的性能优化有哪些方法?
A : 性能优化方法:
特征缓存 :缓存常用特征,减少数据库查询模型压缩 :使用模型量化、剪枝等技术异步处理 :非关键路径异步处理批量推理 :批量处理多个请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import asynciofrom functools import lru_cacheclass OptimizedRecommendationSystem : def __init__ (self ): self.feature_cache = {} self.model_cache = {} @lru_cache(maxsize=10000 ) def get_cached_features (self, user_id ): """缓存用户特征""" return self.compute_features(user_id) async def async_recommend (self, user_id ): """异步推荐""" user_features = await asyncio.to_thread(self.get_cached_features, user_id) item_features = await asyncio.to_thread(self.get_all_item_features) recommendations = self.batch_predict(user_id, user_features, item_features) return recommendations def batch_predict (self, user_id, user_features, item_features_list ): """批量预测""" batch_input = self.prepare_batch(user_features, item_features_list) scores = self.model.batch_predict(batch_input) top_indices = np.argsort(scores)[::-1 ][:20 ] return [item_features_list[i]['id' ] for i in top_indices]
Q8:
如何评估实时推荐系统的效果?
A : 评估指标包括:
在线指标 : CTR 、转化率、 GMV 等业务指标算法指标 :遗憾、准确率、覆盖率系统指标 :延迟、吞吐量、可用性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class RecommendationEvaluator : def __init__ (self ): self.metrics = { 'ctr' : [], 'conversion_rate' : [], 'regret' : [], 'latency' : [] } def evaluate (self, recommendations, user_feedback ): """评估推荐效果""" clicks = sum (1 for item in recommendations if item in user_feedback['clicked' ]) ctr = clicks / len (recommendations) if recommendations else 0 self.metrics['ctr' ].append(ctr) purchases = sum (1 for item in recommendations if item in user_feedback['purchased' ]) conversion = purchases / len (recommendations) if recommendations else 0 self.metrics['conversion_rate' ].append(conversion) return { 'ctr' : ctr, 'conversion_rate' : conversion } def get_summary (self ): """获取评估摘要""" return { 'avg_ctr' : np.mean(self.metrics['ctr' ]), 'avg_conversion_rate' : np.mean(self.metrics['conversion_rate' ]), 'avg_latency' : np.mean(self.metrics['latency' ]) }
Q9: 如何处理多目标优化(如
CTR 和多样性)?
A : 多目标优化方法:
加权求和 :Pareto 优化 :找到 Pareto 前沿两阶段 :先按 CTR 排序,再重排保证多样性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class MultiObjectiveRecommender : def __init__ (self, ctr_weight=0.7 , diversity_weight=0.3 ): self.ctr_weight = ctr_weight self.diversity_weight = diversity_weight def recommend (self, user_id, candidates ): """多目标推荐""" ctr_scores = [self.predict_ctr(user_id, item) for item in candidates] diversity_scores = self.compute_diversity(candidates) combined_scores = [ self.ctr_weight * ctr + self.diversity_weight * div for ctr, div in zip (ctr_scores, diversity_scores) ] sorted_indices = np.argsort(combined_scores)[::-1 ] return [candidates[i] for i in sorted_indices[:20 ]] def compute_diversity (self, items ): """计算多样性分数""" features = [self.item_features[item] for item in items] diversity_scores = [] for i, item in enumerate (items): similarities = [ self.compute_similarity(self.item_features[item], self.item_features[other]) for other in items[:i] ] diversity = 1.0 - np.mean(similarities) if similarities else 1.0 diversity_scores.append(diversity) return diversity_scores
Q10:
实时推荐系统如何保证数据一致性?
A : 保证一致性的方法:
事务处理 :关键操作使用事务版本控制 :特征和模型使用版本号最终一致性 :接受短暂不一致,最终达到一致幂等性 :操作可以重复执行而不改变结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class ConsistentRecommendationSystem : def __init__ (self ): self.feature_versions = {} self.model_version = 0 def update_features (self, user_id, features, version ): """版本化更新特征""" current_version = self.feature_versions.get(user_id, 0 ) if version > current_version: self.user_features[user_id] = features self.feature_versions[user_id] = version return True else : return False def recommend_with_version (self, user_id ): """带版本号的推荐""" user_version = self.feature_versions.get(user_id, 0 ) recommendations = self.recommend(user_id) return { 'recommendations' : recommendations, 'feature_version' : user_version, 'model_version' : self.model_version }
总结
实时推荐与在线学习是推荐系统发展的重要方向。通过流式计算框架(
Flink/Kafka)实现低延迟数据处理,通过 Bandit 算法( UCB 、 Thompson
Sampling)平衡探索与利用,通过上下文 Bandit 和时变偏好建模( HyperBandit
、
B-DES)捕捉用户兴趣演化,最终构建出能够实时响应用户变化的推荐系统。
工业实践中, YouTube
和字节跳动等公司的系统设计为我们提供了宝贵的参考。但每个业务场景都有其特殊性,需要根据数据特点、业务目标和资源约束选择合适的架构和算法。
未来,随着计算能力的提升和算法的改进,实时推荐系统将更加智能和高效,为用户提供更好的个性化体验。