当 ChatGPT 横空出世,大语言模型( LLM)的能力震惊了世界。从文本生成到代码编写,从问答对话到知识推理, LLM 展现出了前所未有的通用智能。那么,这样一个强大的工具能否应用到推荐系统中?答案是肯定的,而且正在发生。
传统的推荐系统依赖协同过滤、矩阵分解、深度学习等方法,它们擅长从用户行为数据中挖掘模式,但往往缺乏对物品语义的深度理解,也难以处理冷启动、可解释性等挑战。 LLM 的出现为推荐系统带来了新的可能性:它能够理解物品的文本描述、用户的历史偏好、甚至生成自然语言的推荐理由。
本文将深入探讨 LLM 在推荐系统中的各种应用方式:从简单的 Prompt-based 推荐,到复杂的端到端架构;从特征增强到重排序,从对话式推荐到可解释推荐。我们会看到 A-LLMRec 、 XRec 、 ChatREC 、 RA-Rec 、 ChatCRS 等前沿架构,理解它们的设计思路,并通过完整的代码实现来掌握这些技术。
LLM 在推荐系统中的角色定位
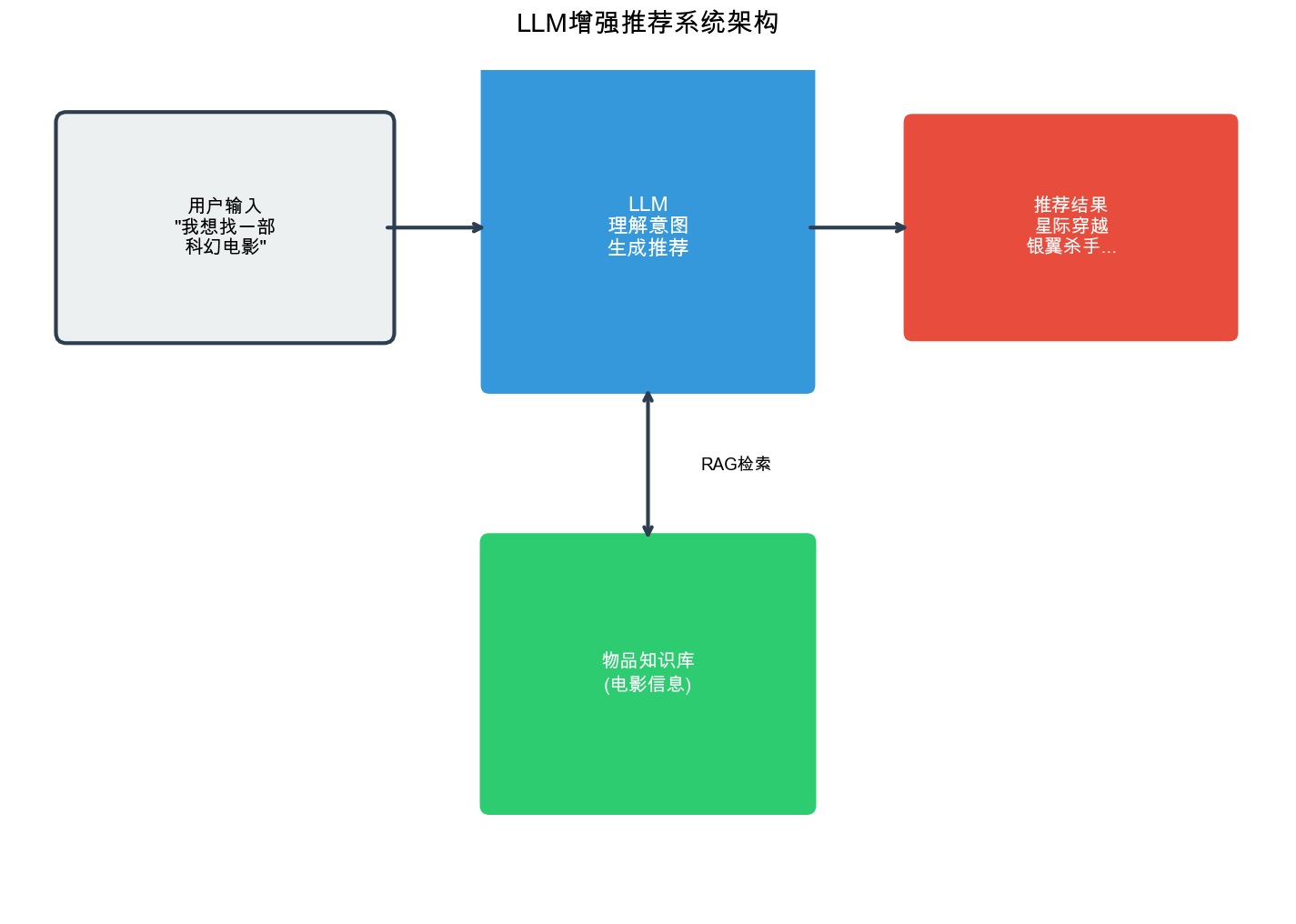
在深入具体架构之前,需要先理解 LLM 在推荐系统中可以扮演哪些角色。这决定了我们如何设计系统架构,以及如何平衡效果和效率。
传统推荐系统的局限
传统的推荐系统(协同过滤、矩阵分解、深度神经网络)主要依赖用户行为数据(点击、购买、评分等)来学习用户偏好和物品特征。这种方法虽然有效,但存在几个根本性局限:
语义理解不足:传统方法难以理解物品的文本描述、用户评论等语义信息。例如,一个电影推荐系统可能知道用户喜欢"动作片",但无法理解"充满悬疑的动作片"和"轻松幽默的动作片"之间的区别。
冷启动问题:新用户或新物品缺乏历史行为数据,传统方法难以做出准确推荐。虽然可以用内容特征缓解,但特征工程往往需要大量人工工作。
可解释性差:深度学习模型是黑盒,难以解释为什么推荐某个物品。用户看到推荐结果时,往往不知道原因,降低了信任度。
跨域迁移困难:在一个领域训练的模型很难迁移到另一个领域,因为不同领域的特征空间差异很大。
LLM 带来的新能力
LLM 通过预训练获得了丰富的世界知识和语言理解能力,为推荐系统带来了新的可能性:
深度语义理解: LLM 能够理解物品的文本描述、用户评论、甚至隐含的语义信息。它可以将"悬疑动作片"和"轻松动作片"区分开来。
零样本推理: LLM 可以在没有训练数据的情况下进行推理。对于新物品,只需要提供文本描述, LLM 就能理解其特性并做出推荐。
自然语言生成: LLM 可以生成推荐理由,用自然语言解释为什么推荐某个物品,大大提升了可解释性。
知识迁移: LLM 的预训练知识可以迁移到不同领域,减少了对领域特定数据的需求。
LLM 在推荐系统中的角色
根据 LLM 在推荐流程中的位置和作用,可以将其分为以下几种角色:
1. 特征增强器( Feature Enhancer)
LLM 用于提取或增强物品和用户的特征表示。例如: - 将物品的文本描述编码为向量 - 从用户评论中提取偏好特征 - 生成物品的语义标签
2. 候选生成器( Candidate Generator)
LLM 直接用于生成推荐候选。例如: - 基于用户历史,用 LLM 生成候选物品列表 - 通过对话理解用户需求,生成推荐
3. 重排序器( Reranker)
LLM 用于对候选物品进行精细排序。例如: - 对粗排后的候选进行语义理解和重排序 - 考虑用户意图和物品语义的匹配度
4. 可解释性生成器( Explanation Generator)
LLM 用于生成推荐理由。例如: - 解释为什么推荐某个物品 - 生成个性化的推荐说明
5. 端到端推荐器( End-to-End Recommender)
LLM 作为完整的推荐系统,从理解用户需求到生成推荐结果。
接下来,我们将深入探讨每种角色的具体实现方式。
Prompt-based 推荐:最简单的 LLM 应用
Prompt-based 推荐是最直观的 LLM 应用方式:将推荐任务转化为自然语言提示,让 LLM 直接生成推荐结果。虽然简单,但在某些场景下效果不错。

基本思路
Prompt-based 推荐的基本思路:将用户的历史行为和物品信息组织成自然语言提示,让 LLM 理解用户偏好并生成推荐。
示例 Prompt:
1 | 用户历史行为: |
实现代码
让我们实现一个完整的 Prompt-based 推荐系统。这个实现展示了如何将推荐任务转化为自然语言提示,让 LLM 理解用户偏好并生成推荐结果。
Prompt-based 推荐的核心设计: 1. Prompt 构建:将用户历史行为和候选物品组织成结构化的自然语言提示 2. 输出格式控制:通过明确的格式要求,确保 LLM 输出可解析的结构化结果 3. 错误处理:处理 LLM 输出可能的不一致性(如添加 markdown 标记)
1 | import json |
Prompt 工程技巧
要让 Prompt-based 推荐效果更好,需要注意以下几点:
1. 结构化输入
将用户历史和候选物品组织成清晰的结构,使用编号、分类等让 LLM 更容易理解。
2. 明确输出格式
指定 JSON 格式输出,便于后续解析。可以使用 few-shot examples 来引导 LLM 输出正确格式。
3. 控制温度参数
推荐任务需要一致性,应该使用较低的温度( 0.1-0.3),而不是创意生成任务的高温度( 0.7-1.0)。
4. 添加约束条件
在 Prompt 中明确约束,例如"不要推荐用户已经看过的电影"、"优先推荐评分高的电影"等。
5. 处理长上下文
如果用户历史很长,需要截断或摘要。可以使用 LLM 先对历史进行摘要,再用于推荐。
优缺点分析
优点: - 实现简单,无需训练模型 - 可解释性强, LLM 会生成推荐理由 - 零样本能力,对新领域也能工作 - 自然语言交互,用户体验好
缺点: - 延迟高,每次推荐都需要调用 LLM API - 成本高, Token 消耗大 - 不稳定,可能生成格式错误的结果 - 难以处理大规模候选集
Prompt-based 推荐适合小规模、对延迟不敏感的场景,或者作为其他方法的补充。接下来,我们将看到更高效的架构设计。
A-LLMRec:适配器增强的 LLM 推荐架构
A-LLMRec( Adapter-enhanced LLM for Recommendation)是一种将 LLM 与传统推荐模型结合的架构。基本思路:使用轻量级的适配器( Adapter)来微调 LLM,使其适应推荐任务,而不是直接使用预训练的 LLM 。
架构设计
A-LLMRec 的架构包含以下几个组件:
- LLM 编码器:使用预训练的 LLM(如 BERT 、 GPT)来编码物品文本和用户历史
- 适配器层:在 LLM 的每一层插入轻量级的适配器,用于任务特定的微调
- 推荐头:将 LLM 的输出映射到推荐分数
适配器机制
适配器是一种参数高效的微调方法。在 Transformer 的每一层中,适配器插入在注意力层和前馈层之后:
其中: -
这样,只需要训练
完整实现
1 | import torch |
优势分析
A-LLMRec 的优势在于:
- 参数高效:只需要训练适配器参数,而不是整个 LLM,大大降低了训练成本
- 知识保留: LLM 的预训练知识得以保留,同时适应推荐任务
- 可扩展性:可以轻松添加新的适配器来处理不同的推荐场景
- 灵活性:可以针对不同层使用不同大小的适配器
XRec:可解释的 LLM 推荐系统
XRec( Explainable Recommendation)专注于使用 LLM 生成可解释的推荐理由。用户不仅看到推荐结果,还能理解为什么推荐这些物品。
架构设计
XRec 包含两个主要组件:
- 推荐模型:生成推荐分数(可以使用任何推荐模型)
- 解释生成器:基于 LLM 生成推荐理由
实现代码
1 | from typing import List, Dict, Tuple |
XRec 的核心价值在于提升推荐系统的可解释性,让用户理解推荐的原因,从而增加信任度和满意度。
LLM 作为特征增强器
LLM 可以作为特征增强器,将物品的文本信息(描述、评论、标签等)编码为高质量的向量表示,然后用于传统的推荐模型。这种方法结合了 LLM 的语义理解能力和传统推荐模型的高效性。
基本思路
使用 LLM 提取特征的基本流程:
- 文本编码:使用 LLM 将物品文本编码为向量
- 特征融合:将 LLM 特征与传统特征( ID 、类别等)融合
- 推荐预测:使用融合后的特征进行推荐
实现代码
1 | import torch |
优势分析
使用 LLM 作为特征增强器的优势:
- 语义理解: LLM 能够理解物品的文本描述,提取丰富的语义特征
- 冷启动友好:对于新物品,即使没有历史行为数据,也可以通过文本描述提取特征
- 可解释性: LLM 特征往往对应语义概念,便于理解
- 灵活性:可以轻松添加新的文本信息(评论、标签等)来增强特征
LLM 作为重排序器
在推荐系统的多阶段架构中,重排序( Reranking)是最后一环。 LLM 可以作为重排序器,对粗排后的候选进行精细排序,考虑用户意图、物品语义等复杂因素。
架构设计
LLM 重排序器的基本流程:
- 候选准备:从粗排阶段获得 Top-K 候选(例如 Top-100)
- 上下文构建:构建包含用户历史、候选物品信息的上下文
- LLM 排序:使用 LLM 对候选进行排序
- 结果输出:返回重排序后的 Top-N 结果
实现代码
{% raw %}1 | from typing import List, Dict, Tuple |
LLM 作为重排序器的优势在于能够考虑复杂的语义匹配和用户意图,但需要注意 Token 消耗和延迟问题。
对话式推荐: ChatREC
对话式推荐( Conversational Recommendation)允许用户通过自然语言对话与推荐系统交互,系统可以理解用户意图、询问澄清问题、提供推荐并解释理由。 ChatREC 是这一领域的代表性架构。
架构设计
ChatREC 的核心组件:
- 对话管理器:管理多轮对话状态
- 意图理解器:理解用户意图(搜索、浏览、澄清等)
- 推荐引擎:基于对话历史生成推荐
- 响应生成器:生成自然语言响应
实现代码
1 | from typing import List, Dict, Optional, Tuple |
ChatREC 实现了自然语言交互的推荐系统,大大提升了用户体验和系统的灵活性。
RA-Rec:检索增强的推荐架构
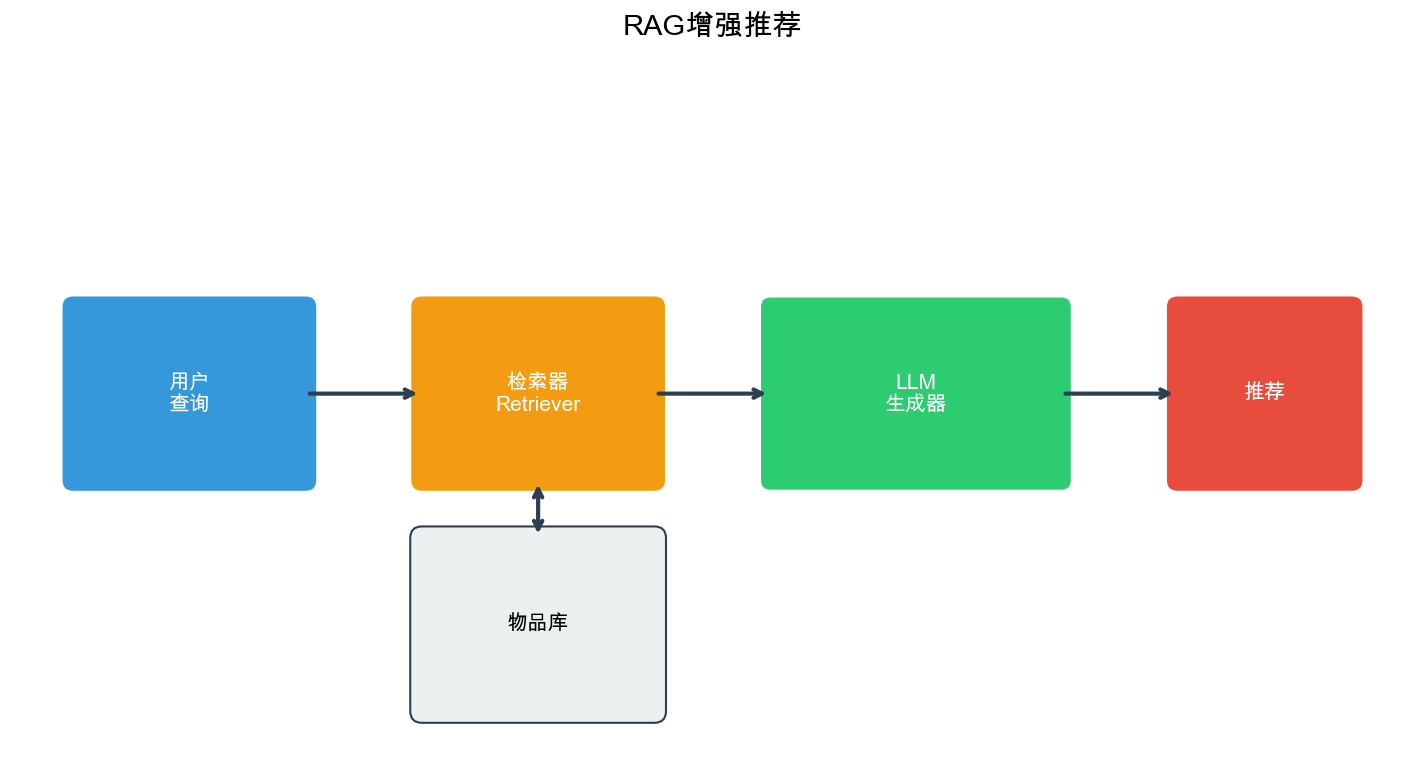
RA-Rec( Retrieval-Augmented Recommendation)结合了检索和生成的优势。它使用检索模块快速找到相关候选,然后使用 LLM 进行精细排序和解释生成。
架构设计
RA-Rec 包含以下组件:
- 检索模块:使用向量检索快速找到相关候选
- LLM 排序器:对检索结果进行精细排序
- 解释生成器:生成推荐理由
实现代码
1 | import numpy as np |
RA-Rec 结合了检索的高效性和 LLM 的语义理解能力,在效果和效率之间取得了平衡。
ChatCRS:对话式推荐系统框架
ChatCRS( Chat-based Conversational Recommendation System)是一个完整的对话式推荐系统框架,集成了意图理解、推荐生成、解释生成等功能。
架构特点
ChatCRS 的特点:
- 多轮对话管理:维护对话状态和历史
- 混合推荐策略:结合多种推荐方法
- 自然语言生成:生成流畅的对话响应
- 个性化适应:根据用户反馈调整推荐
核心实现
1 | from typing import List, Dict, Optional |
ChatCRS 提供了一个完整的对话式推荐框架,可以根据具体需求进行扩展和定制。
Token 效率优化
LLM 在推荐系统中的应用面临一个关键挑战: Token 消耗。每次调用 LLM 都需要消耗大量 Token,成本高昂。需要优化策略来减少 Token 使用。
优化策略
1. 文本摘要
对于长文本(如物品描述、用户评论),先进行摘要再输入 LLM:
1 | def summarize_text(text: str, max_length: int = 100) -> str: |
2. 批量处理
将多个请求合并为批量请求,减少 API 调用次数:
1 | def batch_recommend(queries: List[str], batch_size: int = 10) -> List[List[Dict]]: |
3. 缓存机制
缓存常见查询的结果,避免重复调用 LLM:
1 | from functools import lru_cache |
4. 使用更小的模型
对于某些任务,可以使用更小的模型(如 GPT-3.5-turbo 而不是 GPT-4),在效果和成本之间平衡。
5. 结构化 Prompt
使用结构化的 Prompt 格式,减少冗余信息:
1 | def build_efficient_prompt(user_history: List[Dict], candidates: List[Dict]) -> str: |
6. 两阶段策略
先用小模型/快速方法筛选,再用大模型精细处理:
1 | def two_stage_recommend(user_query: str, all_items: List[Dict]) -> List[Dict]: |
通过这些优化策略,可以显著降低 Token 消耗和成本,同时保持推荐效果。
完整代码示例:端到端 LLM 推荐系统
下面是一个完整的端到端 LLM 推荐系统实现,整合了前面提到的各种技术:
1 | import torch |
常见问题解答( Q&A)
Q1: LLM 推荐系统相比传统推荐系统有什么优势?
A: LLM 推荐系统的主要优势包括:
- 语义理解能力: LLM 能够理解物品的文本描述、用户评论等语义信息,而传统方法主要依赖数值特征
- 零样本能力:对于新物品或新用户, LLM 可以在没有训练数据的情况下进行推理
- 可解释性: LLM 可以生成自然语言的推荐理由,提升用户体验和信任度
- 跨域迁移: LLM 的预训练知识可以迁移到不同领域
- 自然语言交互:支持对话式推荐,用户体验更好
但也要注意 LLM 的劣势:延迟高、成本高、需要大量 Token 。
Q2: 如何平衡 LLM 推荐的效果和效率?
A: 可以采用以下策略:
- 混合架构:使用传统方法进行粗排, LLM 只用于重排序和解释生成
- 检索增强:先用向量检索快速筛选候选,再用 LLM 精细处理
- 缓存机制:缓存常见查询的结果
- 批量处理:将多个请求合并处理
- 模型选择:根据任务复杂度选择合适大小的模型(小任务用小模型)
Q3: LLM 推荐系统如何处理冷启动问题?
A: LLM 推荐系统在冷启动方面有明显优势:
- 新物品冷启动:只需要提供物品的文本描述, LLM 就能理解其特性并做出推荐
- 新用户冷启动:可以通过对话了解用户需求,或者使用 LLM 理解用户的自然语言描述
- 零样本推荐: LLM 的预训练知识使其能够在没有领域特定数据的情况下工作
Q4: Prompt 工程在 LLM 推荐中有多重要?
A: Prompt 工程非常关键,直接影响推荐效果:
- 结构化输入:清晰的组织用户历史和候选物品信息
- 明确输出格式:指定 JSON 等格式,便于解析
- Few-shot 示例:提供示例引导 LLM 输出正确格式
- 约束条件:明确约束(如"不要推荐已看过的")
- 上下文管理:合理控制上下文长度,避免 Token 浪费
Q5: 如何评估 LLM 推荐系统的效果?
A: 评估可以从多个维度进行:
- 离线指标:
- 准确率( Precision)、召回率( Recall)
- NDCG 、 MAP 等排序指标
- 多样性、新颖性等指标
- 在线指标:
- 点击率( CTR)
- 转化率
- 用户满意度
- LLM 特定指标:
- 解释质量(人工评估或自动评估)
- 对话流畅度
- Token 效率
- A/B 测试:与基线系统对比,评估实际业务指标
Q6: LLM 推荐系统的成本如何控制?
A: 成本控制策略:
- Token 优化:
- 文本摘要,减少输入长度
- 结构化 Prompt,避免冗余
- 批量处理,提高效率
- 缓存策略:
- 缓存常见查询
- 缓存物品特征(避免重复编码)
- 模型选择:
- 简单任务用小模型
- 复杂任务用大模型
- 考虑使用开源模型(如 LLaMA)
- 架构优化:
- 只在关键环节使用 LLM
- 其他环节用传统方法
Q7: LLM 推荐系统如何处理用户隐私?
A: 隐私保护措施:
- 数据脱敏:移除敏感信息(如真实姓名、地址)
- 本地部署:使用开源模型本地部署,避免数据上传
- 差分隐私:在训练或推理时添加噪声
- 访问控制:限制对用户数据的访问
- 数据加密:传输和存储时加密
Q8: 如何将 LLM 推荐系统集成到现有系统中?
A: 集成策略:
- 渐进式集成:
- 先作为补充模块(如解释生成)
- 逐步扩展到更多环节
- A/B 测试验证效果
- API 封装:
- 将 LLM 推荐封装为独立服务
- 通过 API 调用,降低耦合
- 降级策略:
- LLM 服务失败时,降级到传统方法
- 设置超时和重试机制
- 监控和日志:
- 监控延迟、错误率、 Token 消耗
- 记录推荐结果,便于分析和优化
Q9: LLM 推荐系统在哪些场景下效果最好?
A: LLM 推荐系统在以下场景效果较好:
- 文本丰富的领域:如书籍、电影、新闻等,有丰富的文本描述
- 冷启动场景:新用户或新物品,缺乏历史数据
- 需要解释的场景:用户希望理解推荐理由
- 对话式交互:用户通过自然语言表达需求
- 跨域推荐:需要在不同领域间迁移知识
但在以下场景可能不如传统方法: - 大规模实时推荐(延迟要求高) - 纯数值特征(如价格、评分) - 成本敏感的场景
Q10: 未来 LLM 推荐系统的发展方向是什么?
A: 未来发展方向:
- 多模态融合:结合文本、图像、音频等多种模态
- 个性化微调:为每个用户微调模型
- 强化学习:使用 RL 优化长期用户满意度
- 知识图谱集成:结合知识图谱提供更丰富的语义信息
- 效率优化:模型压缩、量化、蒸馏等技术
- 可解释性增强:更自然、更准确的解释生成
- 隐私保护:联邦学习、差分隐私等技术
总结
LLM 为推荐系统带来了新的可能性,从简单的 Prompt-based 推荐到复杂的端到端架构,从特征增强到对话式交互, LLM 正在改变推荐系统的面貌。
关键要点:
- LLM 的角色多样:可以是特征增强器、重排序器、解释生成器或端到端推荐器
- 架构设计重要:需要平衡效果和效率,合理使用 LLM
- Prompt 工程关键:好的 Prompt 能显著提升效果
- 成本需要控制:通过缓存、批量处理、模型选择等策略降低成本
- 评估要全面:不仅要看准确率,还要看解释质量、用户体验等
实践建议:
- 从小规模开始,逐步扩展
- 结合传统方法,发挥各自优势
- 重视 Prompt 工程和上下文管理
- 建立完善的监控和评估体系
- 关注成本控制,确保可持续性
LLM 推荐系统仍处于快速发展阶段,新的架构和方法不断涌现。作为推荐系统工程师,需要持续学习,在实践中不断优化和改进。
希望这篇文章能帮助你理解 LLM 在推荐系统中的应用,并为你的实践提供参考。如果你有任何问题或想法,欢迎交流讨论!
- 本文标题:推荐系统(十二)—— 大语言模型与推荐系统
- 本文作者:Chen Kai
- 创建时间:2024-06-26 14:30:00
- 本文链接:https://www.chenk.top/%E6%8E%A8%E8%8D%90%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%EF%BC%88%E5%8D%81%E4%BA%8C%EF%BC%89%E2%80%94%E2%80%94-%E5%A4%A7%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B%E4%B8%8E%E6%8E%A8%E8%8D%90%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F/
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!